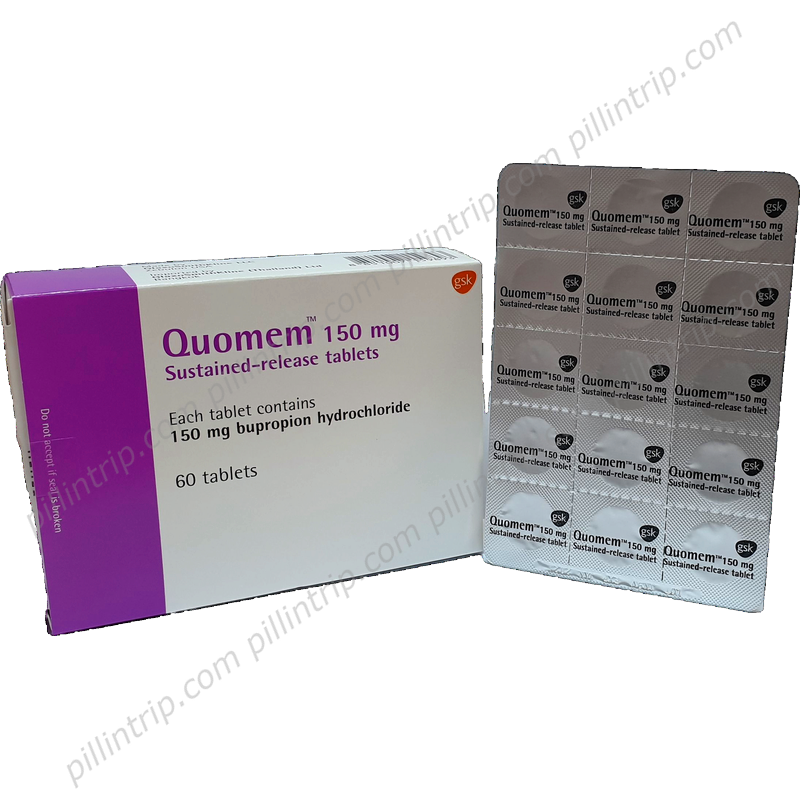
Quomem
重要なセクションへのクイックリンク
Quomem
Medically reviewed
Last updated on 1/10/2026
このページは、公式な医療情報源から収集された、一般的で参考レベルの情報を提供しています。これは、専門的な医療アドバイス、診断、治療に代わるものではありません。健康に関する判断を行う際には、必ず資格を有する医療専門家にご相談ください。
Quomemの概要
Quomemで起こり得る副作用
過量投与および緊急時の対応
Quomemの治療上の用途
使用適格性および使用上の制限
他の医薬品との相互作用について知っておくべきこと
作用機序
用法・用量に関する情報
最新の臨床エビデンス
よくある質問(FAQ)
Quomemの保管および廃棄方法
注意! 丸薬や薬を使用する前に、常に医師または薬剤師に相談してください。
国で利用可能です:
Quomemに相当します:
 Portugal
Portugal Russia
Russia Mexico
Mexico Colombia
Colombia Cyprus
Cyprus India
India Czech Republic
Czech Republic Georgia
Georgia Lebanon
Lebanon Bosnia & Herzegowina
Bosnia & Herzegowina Israel
Israel Canada
Canada Denmark
Denmark USA
USA Argentina
Argentina Belgium
Belgium Norway
Norway Switzerland
Switzerland Indonesia
Indonesia South Korea
South Korea Bulgaria
Bulgaria Turkey
Turkey Malasia
Malasia Finland
Finland Bangladesh
Bangladesh China
China Brasil
Brasil Ukraine
Ukraine Vietnam
Vietnam Spain
Spain Phillipines
Phillipines United Kingdom
United Kingdom Costa Rica
Costa Rica Tunisia
Tunisia Greece
Greece Sweden
Sweden Macedonia
Macedonia Hong Kong
Hong Kong Serbia
Serbia Japan
Japan Kenya
Kenya South Africa
South Africa Oman
Oman Germany
Germany Belize
Belize Poland
Poland Egypt
Egypt Italy
Italy Taiwan
Taiwan Austria
Austria France
France Venezuela
Venezuela Malta
Malta Ecuador
Ecuador Australia
Australia Chile
Chile Lithuania
Lithuania Latvia
Latvia Trinidad & Tobago
Trinidad & Tobago Bahrain
Bahrain Peru
Peru Hungary
Hungary New Zealand
New Zealand Slovakia
Slovakia Myanmar
Myanmar Singapore
Singapore Pakistan
Pakistan Croatia (Hrvatska)
Croatia (Hrvatska) Estonia
Estonia Romania
Romania Slovenia
Slovenia