Merapur
Links rápidos para seções importantes
Merapur
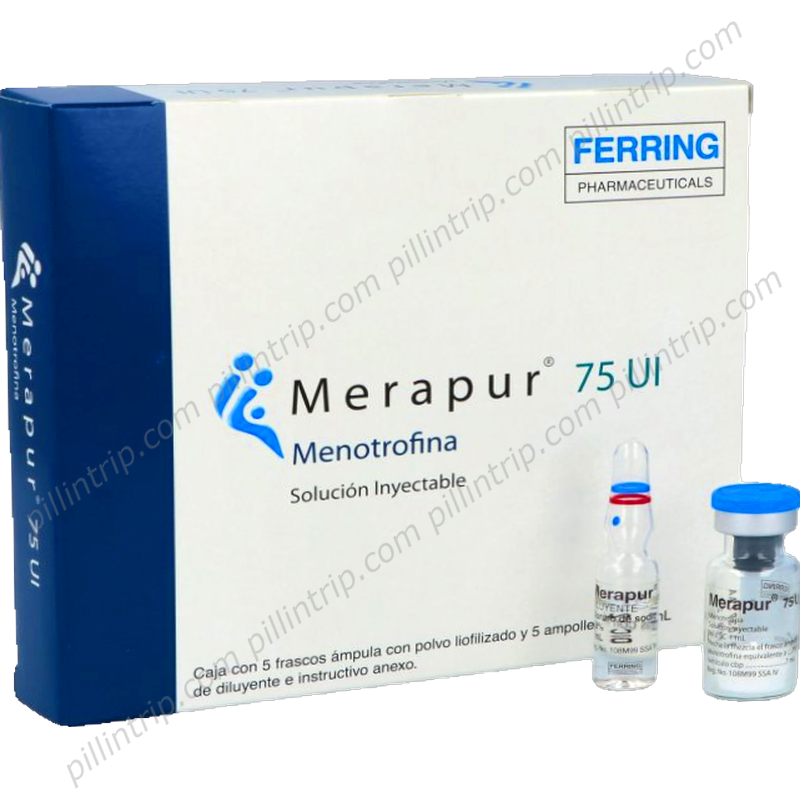
Método de ação:
Opção de tratamento:
Medically reviewed
Last updated on 1/10/2026
Esta página fornece informações gerais e de referência compiladas a partir de fontes médicas oficiais. Não substitui aconselhamento médico profissional, diagnóstico ou tratamento. Para decisões sobre a sua saúde, consulte um profissional de saúde qualificado.
Visão geral de Merapur
Quais efeitos secundários são possíveis com Merapur?
Sobredosagem e resposta em caso de emergência
Usos terapêuticos de Merapur
Critérios de utilização e restrições
O que devo saber sobre interações com outros medicamentos?
Mecanismo de ação
Informações sobre dosagem e administração
Evidência clínica recente
Perguntas frequentes (FAQ)
Como Merapur deve ser armazenado e descartado?
Atenção! Sempre consulte um médico ou farmacêutico antes de usar pílulas ou medicamentos.
Disponível em países:
Equivalente a Merapur encontrado em:
 Portugal
Portugal Russia
Russia Colombia
Colombia Cyprus
Cyprus India
India Czech Republic
Czech Republic Georgia
Georgia Lebanon
Lebanon Bosnia & Herzegowina
Bosnia & Herzegowina Israel
Israel Canada
Canada Denmark
Denmark USA
USA Argentina
Argentina Belgium
Belgium Norway
Norway Thailand
Thailand Switzerland
Switzerland Indonesia
Indonesia South Korea
South Korea Bulgaria
Bulgaria Turkey
Turkey Malasia
Malasia Finland
Finland Bangladesh
Bangladesh China
China Brasil
Brasil Ukraine
Ukraine Vietnam
Vietnam Spain
Spain Phillipines
Phillipines United Kingdom
United Kingdom Costa Rica
Costa Rica Tunisia
Tunisia Greece
Greece Sweden
Sweden Macedonia
Macedonia Hong Kong
Hong Kong Serbia
Serbia Japan
Japan Kenya
Kenya South Africa
South Africa Oman
Oman Germany
Germany Belize
Belize Poland
Poland Egypt
Egypt Italy
Italy Taiwan
Taiwan Austria
Austria France
France Venezuela
Venezuela Malta
Malta Ecuador
Ecuador Netherlands
Netherlands Australia
Australia Chile
Chile Lithuania
Lithuania Latvia
Latvia Trinidad & Tobago
Trinidad & Tobago Bahrain
Bahrain Peru
Peru Hungary
Hungary New Zealand
New Zealand Slovakia
Slovakia Myanmar
Myanmar Singapore
Singapore Pakistan
Pakistan Croatia (Hrvatska)
Croatia (Hrvatska) Estonia
Estonia Romania
Romania Slovenia
Slovenia